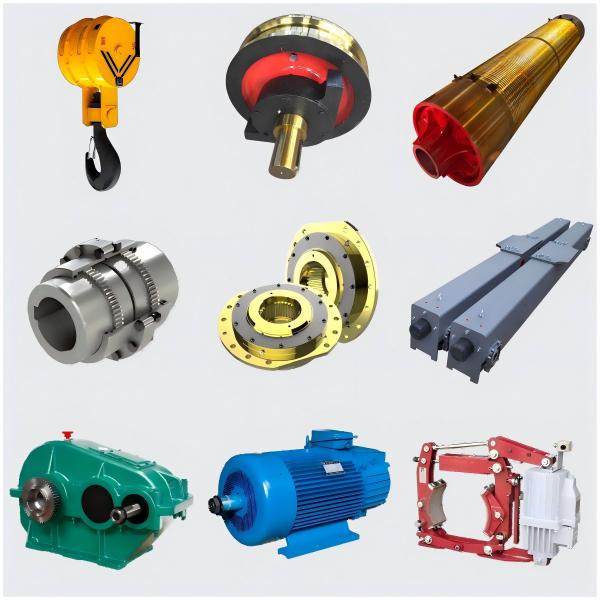
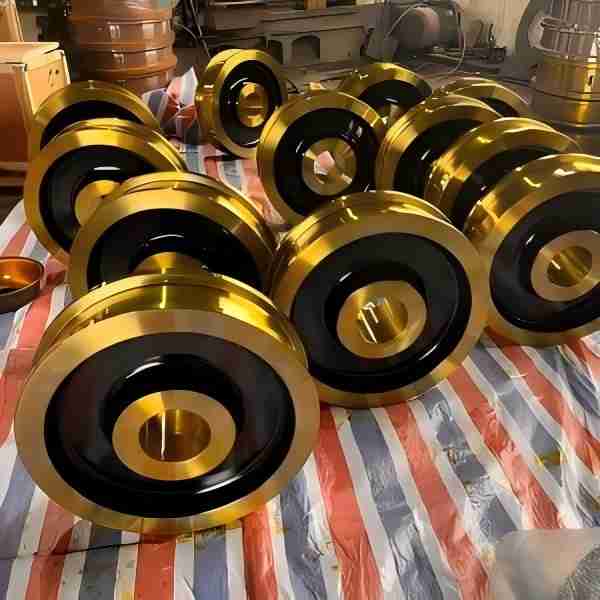
What Causes Unexpected Maintenance Costs in Crane Wheels and Hooks?
In overhead cranes and gantry cranes, crane wheels and hooks are critical load-bearing components. Unexpected maintenance costs related to these parts can lead to unplanned downtime, safety risks, and increased operating expenses. Understanding the root causes of premature wear or failure is essential for crane owners, maintenance teams, and procurement managers.
At HL CRANE, we have seen that most unexpected maintenance issues are not random—they are preventable.
1. Material Fatigue and Poor Metallurgy
One of the most common causes of unexpected maintenance costs is material fatigue. Crane wheels and hooks are subjected to cyclic loads over long periods. If the steel grade, heat treatment, or forging process is inadequate, micro-cracks can develop and eventually lead to failure.
Low-quality materials or inconsistent heat treatment may reduce initial costs but often result in higher lifecycle costs. Using certified materials such as forged alloy steel hooks and heat-treated wheel treads significantly improves durability.
👉 Learn more about our heavy-duty components on the HL CRANE Crane Parts page (internal link).
2. Overloading and Improper Load Distribution
Overloading remains a hidden but costly issue. Even when the crane’s rated capacity is respected, uneven load distribution or side pulling can overstress hooks and wheels.
Common problems include:
-
Hook throat opening due to overload
-
Wheel flange cracking from lateral forces
-
Accelerated bearing and axle wear
Regular load monitoring and operator training can prevent these issues and reduce unplanned maintenance.
3. Rail Misalignment and Installation Errors
For crane wheels, rail alignment is a critical but often overlooked factor. Misaligned rails cause abnormal contact between wheel tread and rail, leading to:
-
Uneven wheel wear
-
Flange damage
-
Increased rolling resistance and motor load
Even high-quality wheels will fail prematurely if installation tolerances are not met. Periodic rail inspection and alignment checks can significantly reduce maintenance frequency.
4. Inadequate Lubrication and Poor Maintenance Practices
Insufficient or incorrect lubrication can dramatically shorten the service life of crane wheels and hooks. Dry bearings, contaminated grease, or incorrect lubrication intervals result in:
-
Increased friction and heat
-
Accelerated bearing failure
-
Corrosion in hook pins and sheaves
A preventive maintenance schedule, rather than reactive repairs, is one of the most cost-effective ways to control long-term expenses.
5. Lack of Regular Inspection and Compliance
International standards such as ISO 4309 and DIN 15401/15402 clearly define inspection requirements for crane hooks and lifting components. Skipping inspections may save time in the short term but often leads to sudden failures and emergency repairs.
You can refer to general lifting safety guidelines from the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) for best practices (external link: https://www.iso.org).
How to Reduce Unexpected Maintenance Costs
To minimize unplanned expenses:
-
Choose reliable crane spare parts manufacturers
-
Use certified materials and proven designs
-
Perform regular inspections and lubrication
-
Replace worn components before failure
At HL CRANE, we supply crane wheels, hooks, drums, couplings, and end carriages designed for long service life and stable performance under heavy-duty conditions.
Final Thoughts
Unexpected maintenance costs in crane wheels and hooks are usually the result of material issues, improper use, installation errors, or insufficient maintenance. By addressing these root causes early, crane owners can significantly reduce downtime and improve operational safety.
If you are looking for durable, cost-effective crane components, HL CRANE is ready to support your project.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. How often should crane wheels and hooks be inspected?
Crane wheels and hooks should be visually inspected daily or before each shift and undergo a detailed inspection every 3 to 6 months, depending on crane duty class and working conditions. Heavy-duty or high-cycle cranes require more frequent inspections to prevent unexpected failures.
2. What are the early signs of crane hook failure?
Common early warning signs include hook throat opening, visible cracks, excessive wear at the saddle, deformation, and corrosion. Any hook showing permanent deformation or cracks should be removed from service immediately to avoid safety hazards.
3. Can poor rail alignment increase crane wheel maintenance costs?
Yes. Poor rail alignment causes uneven wheel tread wear, flange cracking, and increased rolling resistance, which significantly shortens wheel service life. Correct rail installation and periodic alignment checks are essential for reducing long-term maintenance costs.
4. Does using low-cost crane spare parts really increase maintenance expenses?
In most cases, yes. Low-cost spare parts often use inferior materials or improper heat treatment, leading to premature wear and frequent replacements. High-quality, certified components usually offer lower total lifecycle costs, even if the initial price is higher.
5. How can I reduce unexpected downtime caused by crane wheel and hook failures?
You can reduce unexpected downtime by implementing preventive maintenance programs, ensuring proper lubrication, avoiding overloading, and sourcing parts from reliable manufacturers like HL CRANE. Early replacement of worn components is far more cost-effective than emergency repairs.